Regions are used to assign geolocations to Stores, Salespeople, or Purchasing Agents. Customers and Vendors that have addresses that fall within these geolocations can be automatically assigned to a Store, Salesperson or Purchasing Agent.
Regions are configured by giving the region a name, specifying which salesperson or store is assigned to that region, then adding cities and counties into that region.
Regions can be used online, but need to be configured in ITrack Enterprise Desktop at this time.
Three different kinds of Regions can be assigned, Store Regions, Sales Regions, and Purchase Regions.
📍 Store Regions
Store Regions are used to automatically assign a customer to a store based on the customer’s address. It might make sense to assign Store Regions when you have more than one store that serves customers, and you have users who log in to multiple stores.
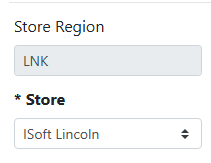
When a customer’s Billing Address City matches a city in the Store Region, the region name is shown in the Store Region field and can’t be edited.
In this example, this customer’s address is in Omaha, which is in my OMA region and assigned to my Omaha store. The customer’s default store was set to ISoft Omaha.
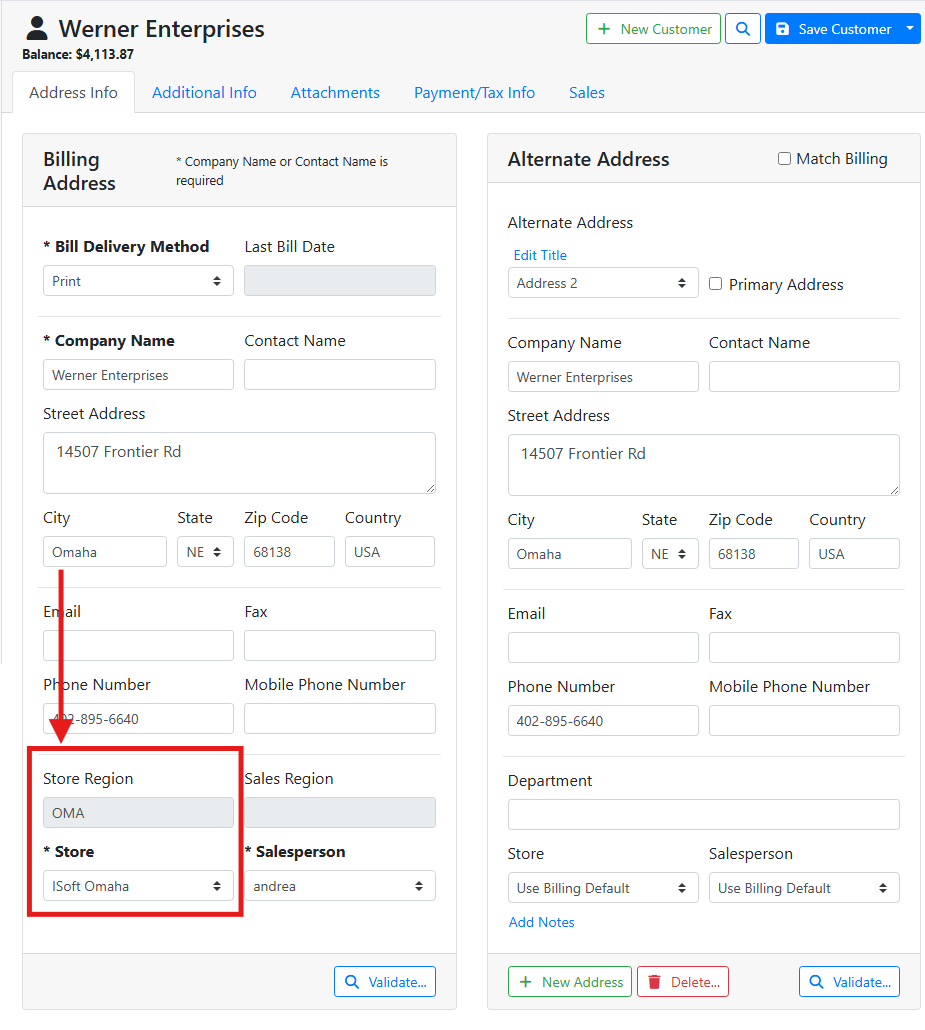
If Store Regions are not configured, or if the customer’s address is not entered, or if the customer’s address doesn’t match a Store Region, the default store assigned to the customer will be the store the user was logged into when creating the customer.
Regardless of how the Store gets assigned to the customer, it can be changed later by a user who has the Edit salesman/store User Permission.
Read more about User Permissions.
📍 Sales Regions
Sales Regions are used to automatically assign a customer to a salesperson based on the customer’s address. It might make sense to assign Sales Regions when your salespersons are assigned customers geographic territories and don’t share customers. The Salesperson on a customer will assign that salesperson by default on new Sales Orders.
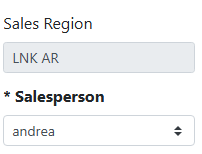
When a customer’s Billing Address City matches a city in the Sales Region, the region name is shown in the Sales Region field and can’t be edited.
In this example, this customer’s address is in Milford, which is a rural town in my LNK AR region and assigned to salesperson andrea.
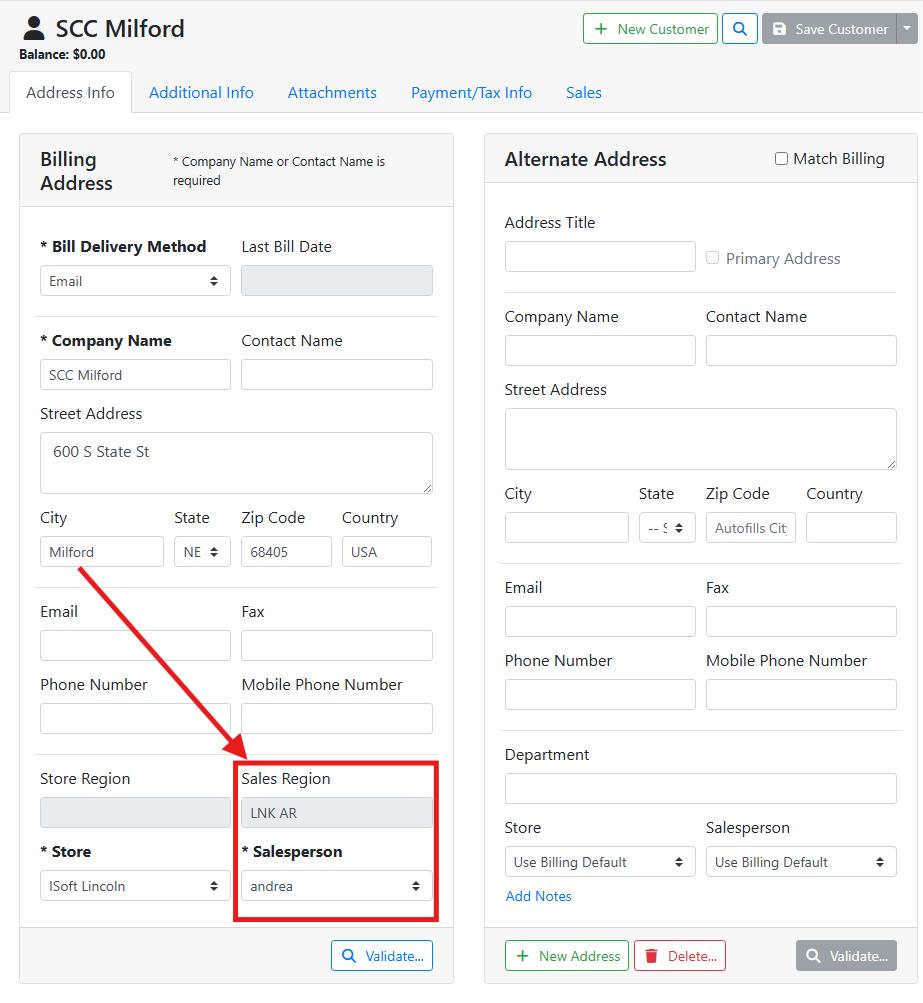
If Sales Regions are not configured, or if the customer’s address is not entered, or if the customer’s address doesn’t match a Sales Region, the default salesperson assigned to the customer will be the user who created the customer, if they are a salesperson. If the user who created the customer was not a salesperson, the first salesperson in the list alphabetically will get assigned, and the user should pick the correct salesperson.
Regardless of how the salesperson gets assigned to the customer, it can be changed later by a user who has the Edit salesman/store User Permission.
Read more about User Permissions.
📍 Purchase Regions
Purchase Regions are used to automatically assign a vendor to a Purchase Agent based on the vendor’s address. It might make sense to assign Purchase Regions when your purchase agents are assigned vendor geographic territories and don’t share vendors.
If the user does not have the permission Search other purchase agents' vendors, they will only be able to see and use vendors that are assigned to them, or not assigned to anyone.
Read more about User Permissions.
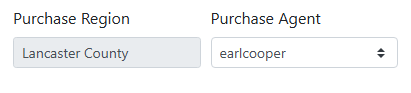
When a vendor's Billing Address City matches a city in the Purchase Region, the region name is shown in the Purchase Region field and can’t be edited.
In this example, this vendor’s address is in Lincoln, which is in my Lancaster County region and assigned to purchase agent earlcooper.
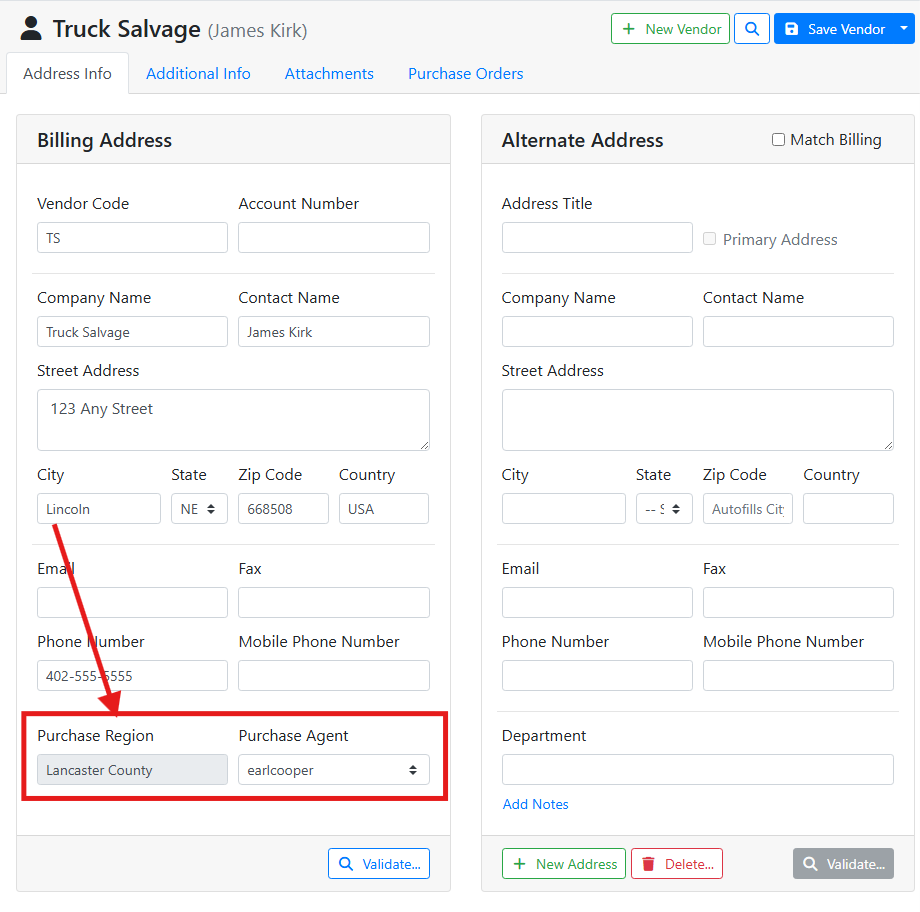
If Purchase Regions are not configured, or if the vendor’s address is not entered, or if the vendor’s address doesn’t match a Purchase Region, a Purchase Agent will not be automatically assigned. A user will need to pick a Purchase Agent manually.
📎 Related Articles
Stores, Locations, and Regions
